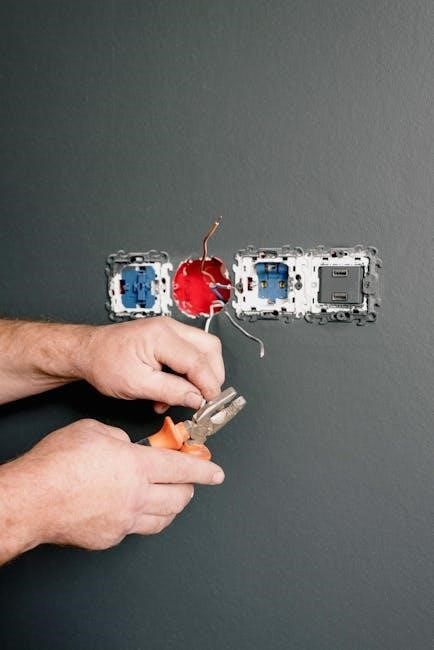
Electrical conduit installation is essential for modern electrical systems, providing protection for wires from damage and environmental factors. This guide ensures safe, code-compliant setups, covering basics to advanced methods and compliance, while preventing electrical hazards and supporting various applications.
1.1 Overview of Electrical Conduit Systems
Electrical conduit systems are designed to protect and route electrical wires safely within buildings or underground. They consist of tubes, fittings, and accessories that encase wires, ensuring protection from environmental factors, mechanical damage, and fire hazards. Conduit materials vary, including PVC, metal, and others, each offering unique benefits like durability, flexibility, or resistance to chemicals. These systems are essential for maintaining electrical integrity, reducing fire risks, and complying with safety standards. Properly installed conduits support efficient electrical distribution, adapt to various environments, and provide long-term reliability for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They are a critical component in modern electrical infrastructure, ensuring safe and efficient power distribution.
1.2 Importance of Proper Installation
Proper installation of electrical conduit systems is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance with electrical codes. Correctly installed conduits prevent wire damage, reduce fire hazards, and minimize the risk of electrical shocks or failures. They also protect against environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. Proper installation ensures efficient electrical distribution and supports long-term system performance. Compliance with standards like the National Electric Code (NEC) is essential to avoid legal issues and ensure system safety. Poor installation can lead to premature wear, increased maintenance costs, and potential hazards. Therefore, adhering to best practices and guidelines is vital for a safe and durable electrical setup, protecting both people and property.

Materials and Tools Required
Electrical conduit installation requires materials like PVC or metallic conduits, fittings, and essential tools such as conduit cutters, benders, and sealants to ensure secure and durable connections.
2.1 Types of Conduit Materials (PVC, Metal, etc.)
Conduit materials vary to suit different applications. PVC conduit is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for underground or wet locations. Metallic conduit, made from steel or aluminum, offers high strength and durability, suitable for industrial settings. Other options include flexible conduits for tight spaces and fiber-optic conduits for data transmission. Each material has specific advantages, ensuring optimal protection and performance for electrical wiring systems. Proper selection based on environmental conditions and load requirements is crucial for a safe and efficient installation. Always choose materials that meet local and international electrical standards for compliance and reliability.
2.2 Essential Tools for Conduit Installation
Various tools are required for a successful conduit installation. A conduit cutter or hacksaw is needed for cutting PVC or metal conduits to the desired length. A conduit bender is essential for creating precise bends without damaging the material. A drill press or hand drill is used for making holes in walls or surfaces for conduit passage. Additionally, a pipe threading machine is necessary for creating threads on metal conduits. A cable feeder or fish tape helps in pulling wires through the conduit. Hand tools like screwdrivers, wrenches, and pliers are indispensable for securing fittings and connections. A laser level ensures accurate placement, while a tape measure and spirit level aid in precise installations. A conduit tester may also be used to verify the integrity of the system post-installation.

Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Always adhere to safety guidelines, wear PPE, and follow best practices to minimize risks. Ensure proper grounding, avoid overloading circuits, and maintain a clean workspace for safe conduit installation.
3.1 General Safety Guidelines
Adhering to general safety guidelines is crucial during electrical conduit installation. Always disconnect power before starting work to prevent electrical shocks or accidents. Use appropriate tools and ensure the workspace is well-ventilated. Properly secure ladders and scaffolding to avoid falls. Never overload circuits, as this can cause overheating and fires. Keep flammable materials away from the work area. Regularly inspect tools and equipment for damage. Ensure all conduit connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing. Follow the National Electric Code (NEC) and local regulations for specific safety requirements. Proper training and supervision are essential, especially for inexperienced personnel. Maintaining a clean and organized workspace reduces tripping hazards and ensures efficiency. Safety should never be compromised to save time or resources.
3.2 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is vital for safety during electrical conduit installation. Essential items include hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toe boots to protect against falling objects, electrical arcs, and sharp edges. Face shields or goggles are recommended when cutting or drilling to prevent eye injury from debris. Insulated tools and voltage-rated gloves should be used when working with live circuits to prevent electrical shock. Respiratory protection, such as dust masks, may be necessary when handling materials that generate dust. Ensure all PPE meets industry standards and is regularly inspected for damage. Properly maintained PPE significantly reduces the risk of accidents and ensures compliance with safety regulations.

Planning and Design Considerations
Effective planning ensures a safe and efficient electrical conduit installation. Assess the site, determine requirements, and create a detailed plan. Always comply with NEC and local standards.
4.1 Assessing the Site and Requirements
Assessing the site and requirements is crucial for a successful electrical conduit installation. Begin by evaluating the environment, including whether the installation is underground or above ground, and the conditions such as temperature, moisture, and exposure to chemicals. Determine the load requirements to choose the appropriate conduit size and material. Identify the type of wires to be used and their ampacity. Consider the local building codes, NEC standards, and any specific regulations for the location. Measure the distances between connection points to calculate the length of conduit needed. Check for any existing infrastructure that may interfere with the installation. Document all findings to ensure a comprehensive plan. Proper assessment ensures compliance and safety.
4.2 Creating a Detailed Installation Plan
Creating a detailed installation plan is vital for organizing and executing the electrical conduit installation efficiently. Start by outlining the sequence of tasks, from preparing the site to final testing. Include specific details such as the layout of the conduit runs, the number and location of supports, and the types of fittings required. Use diagrams or schematics to visualize the system, ensuring clarity for all involved. List the materials needed and their quantities, and identify potential challenges or obstacles. Develop a timeline to manage the project effectively, considering factors like labor availability and equipment usage. Ensure the plan complies with local regulations and safety standards. A well-structured plan minimizes delays and ensures a smooth, error-free installation process. Proper documentation also aids in future maintenance and upgrades.

Types of Electrical Conduits
Electrical conduits vary in materials and applications, offering solutions for different environments. Common types include PVC, flexible, and metallic conduits, each providing unique benefits for durability, flexibility, and protection in various electrical systems.
5.1 PVC Conduit
PVC conduit is a popular choice for electrical installations due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in both residential and commercial settings, offering flexibility and ease of installation. PVC conduit systems are ideal for underground and above-ground applications, providing excellent protection against environmental factors. They are also resistant to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for harsh environments. PVC conduit is available in various sizes and is compatible with a range of fittings and connectors, ensuring a secure and reliable electrical system. Proper installation of PVC conduit requires adherence to local electrical codes and standards, such as those outlined in the National Electric Code (NEC).

5.2 Metallic Conduit
Metallic conduit is a durable and robust option for electrical installations, offering superior strength and protection for wires. It is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where mechanical durability is critical. Available in materials like steel and aluminum, metallic conduit provides excellent resistance to damage from impact and fire. Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 are the most common types, with Schedule 80 offering thicker walls for added protection. Metallic conduit requires proper grounding to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes. Installation involves threading and coupling, which demands precise tools and techniques. While it is heavier and more challenging to install than PVC, metallic conduit is ideal for high-traffic areas and applications requiring maximum durability and fire resistance.
Installation Steps
Electrical conduit installation involves preparing, running, and securing the conduit, ensuring compliance with safety standards and proper techniques for a reliable and durable electrical system setup.
6.1 Preparing the Conduit
Preparing the conduit is the first step in electrical installation. Cut the conduit to the required length using a hacksaw, pipe cutter, or power saw. Ensure cuts are clean and deburr the edges to prevent damage to wires. Clean the conduit thoroughly to remove any debris or residue. Measure and mark the conduit for accurate fitting installation. Align the conduit sections properly, ensuring they are straight and free from bends. Check for any damage or defects before proceeding. Refer to the installation manual for specific guidelines on conduit preparation, including materials and tools recommended for optimal results and compliance with safety standards.
6.2 Running the Conduit
Running the conduit involves installing it along the designated route. Plan the pathway to avoid obstacles and ensure compliance with local codes. Use supports and hangers to secure the conduit at intervals specified by the NEC. For PVC conduit, supports should be lighter due to its lower weight compared to metallic conduit. Ensure the conduit is straight and properly aligned to prevent kinking or damage. Use conduit fittings such as elbows, tees, and couplings to make turns or connections. Apply sealants or weatherproof gaskets where necessary to maintain integrity. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for fitting installation and consider environmental factors like temperature and humidity. Properly running the conduit ensures safe and efficient cable management, meeting both functional and safety requirements.
6.3 Securing the Conduit
Securing the conduit is critical to ensure stability and longevity. Use appropriate fasteners like conduit clips, hangers, or straps, spaced according to NEC guidelines (e.g., Table 352.30 for PVC conduit). Supports should be durable and suitable for the conduit material. For metallic conduit, use heavy-duty hangers, while PVC conduit may require lighter supports due to its weight. Ensure the conduit is tightly fastened to prevent movement or sagging. In areas exposed to harsh conditions, apply additional protection like sealants or weatherproof gaskets. Regularly inspect the conduit and its fasteners to maintain integrity. Proper securing ensures compliance with safety standards and prevents damage from environmental factors or mechanical stress, guaranteeing reliable electrical system performance.
Compliance and Standards
Compliance with NEC and local standards is crucial for safe and reliable electrical conduit installations. Adherence to specific material standards ensures durability and code-compliant protection for wires.
7.1 National Electric Code (NEC) Requirements
The National Electric Code (NEC) sets strict standards for electrical conduit installations, ensuring safety and reliability. Compliance with NEC guidelines is mandatory for all installations, covering aspects such as material selection, conduit sizing, and spacing. Properly securing conduits and ensuring they meet temperature and load requirements is essential. NEC Table 352.30 provides specific support charts for PVC and metallic conduits, considering factors like air temperature and conductor heat. Adhering to these standards prevents hazards and ensures systems operate efficiently. Installers must familiarize themselves with the latest NEC revisions to meet current regulations, guaranteeing safe and durable electrical setups across residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
7.2 Local and International Standards
Beyond NEC, local and international standards must be considered for conduit installations. The IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671) and NEMA guidelines provide additional frameworks, ensuring compliance in diverse regions. These standards address specific environmental conditions, such as weather resistance and fire safety, and dictate appropriate materials and practices. For instance, PVC conduit supports may differ from metallic ones due to weight variations. International standards often align with local codes but may introduce unique requirements, necessitating thorough research. Compliance with these regulations ensures installations meet global safety benchmarks, making them suitable for various markets and applications. Adherence to both local and international standards is crucial for legal and operational compliance, guaranteeing system longevity and safety.
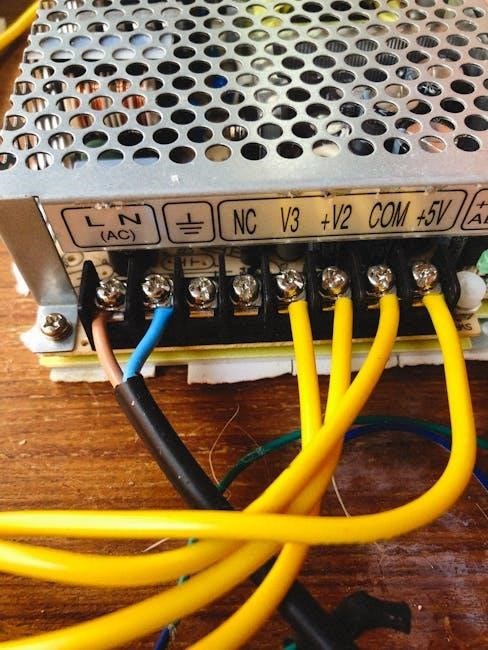


Best Practices for a Successful Installation
Adhering to best practices ensures a safe and efficient electrical conduit installation. Proper sealing, regular testing, and following NEC guidelines are crucial for system reliability and longevity. Compliance with local and international standards, like IET Wiring Regulations, further enhances safety and ensures legal adherence. Using appropriate tools and materials, such as Marshall-Tufflex accessories, simplifies the process. Regular inspections and maintaining detailed installation plans prevent potential issues. These practices not only meet code requirements but also protect against environmental factors, ensuring a durable and hazard-free electrical system.
8.1 Proper Sealing and Protection
Proper sealing and protection are critical for maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical conduit systems. Common methods include using sealant compounds, weatherproof gaskets, and expansion foam, tailored to the environment and conduit type. For instance, in outdoor settings, weatherproof materials ensure resistance against moisture and temperature fluctuations. Sealing prevents water ingress, which can lead to corrosion and electrical hazards. Additionally, employing conduit fittings designed for specific conditions enhances system durability. Regular inspections of seals and connections are essential to maintain protection throughout the installation’s lifecycle. This step ensures compliance with standards like NEC and IET Wiring Regulations, safeguarding against environmental and operational stressors while ensuring reliable electrical performance over time.
8.2 Testing and Inspection
Testing and inspection are vital to ensure the electrical conduit system functions safely and efficiently. After installation, conduct a thorough visual inspection to verify conduit supports, connections, and seals are intact. Perform continuity tests to confirm proper wire connections and insulation resistance tests to identify any faults. Voltage testing ensures the system operates within safe parameters. Inspections should also check for compliance with NEC and IET Wiring Regulations. Regular maintenance inspections are recommended to detect potential issues early. Use tools like multimeters and megohmmeters for accurate readings. Proper testing and inspection prevent electrical hazards, ensure system reliability, and extend the lifespan of the installation. Compliance with these steps guarantees a safe and durable electrical setup.
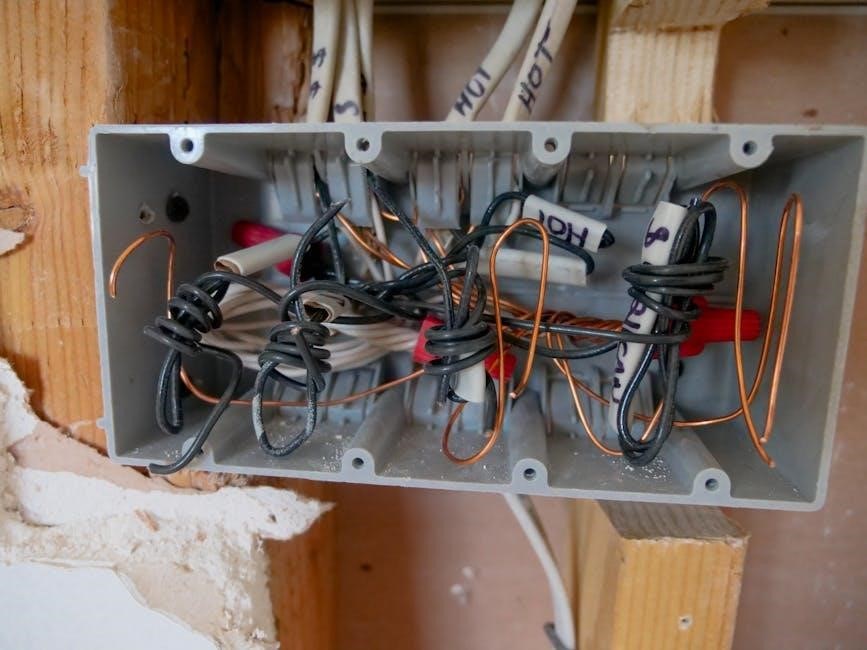
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identify common installation issues like improper sealing, overloading, or inadequate supports. Verify conduit integrity, check for damage, and ensure compliance with NEC and IET standards.
9.1 Identifying and Solving Installation Problems
Common issues during conduit installation include improper sealing, overloading, or environmental damage. Inspect for cracks, dents, or misaligned fittings. Verify conduit integrity and ensure compliance with NEC and IET standards. Address water ingress by applying sealants or weatherproof gaskets. For overloaded systems, redistribute wires or upgrade conduit size. Consult installation manuals for specific solutions. Use expansion foam or fittings to address thermal expansion. Regular testing and inspections can prevent future problems. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for repairs and replacements. Proper documentation of issues and solutions ensures long-term system reliability and safety.
