Understanding Chord Progressions
Chord progressions form the harmonic backbone of songs. Understanding how to construct and analyze them unlocks songwriting and improvisation. Diatonic progressions use chords within a key, while non-diatonic progressions incorporate chords from outside the key, adding color and complexity. Mastering chord progressions enhances musical creativity. Explore resources like guitar chord progression PDFs and online tutorials to deepen your knowledge.
What are Chord Progressions?
A chord progression is a sequence of chords played in a specific order, forming the harmonic structure of a musical piece. Think of it as the foundation upon which melodies and rhythms are built. These progressions can be simple, using only a few chords, or incredibly complex, incorporating numerous chords and intricate harmonic movements. They dictate the mood, feel, and overall character of a song. Understanding chord progressions is crucial for musicians of all levels, from beginners learning basic song structures to advanced players composing original music. Many resources, such as guitar chord progression PDFs and online tutorials, provide detailed explanations and examples, allowing you to explore a vast array of progressions, from the classic four-chord pop progression to more sophisticated jazz and classical arrangements. The ability to analyze and create your own progressions significantly boosts your musical skills.
Constructing Chord Progressions⁚ Diatonic and Non-Diatonic Chords
Building chord progressions involves selecting chords based on their relationship to a key’s scale. Diatonic chords are derived directly from the key’s notes, creating a harmonious and predictable sound. These progressions often feel stable and resolve naturally. Conversely, non-diatonic chords are borrowed from outside the key, introducing tension and unexpected harmonic twists. They can add color, spice, and a sense of movement to a progression. The careful use of non-diatonic chords can create dramatic shifts in mood or lead to surprising resolutions. Many online resources, including guitar chord progression PDFs, detail how to construct both types of progressions using Roman numeral analysis, providing a framework for understanding chord function and relationships within a key. Experimenting with both diatonic and non-diatonic approaches allows for a greater range of harmonic possibilities in your compositions and improvisations.
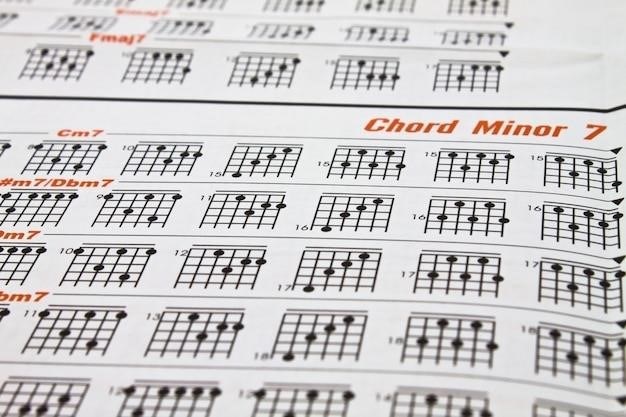

Commonly Used Chord Progressions
This section explores frequently used chord progressions, including the ubiquitous “four chords of pop” and other diatonic and non-diatonic patterns. Many examples can be found in readily available guitar chord progression PDFs and online tutorials.
The Four Chords of Pop (I, IV, V, vi)
The deceptively simple I-IV-V-vi progression, often referred to as the “four chords of pop,” forms the foundation of countless popular songs across various genres. Its effectiveness lies in its inherent musicality and ease of memorization. The progression’s versatility allows for both major and minor key interpretations, offering a wide range of emotional expression. Numerous guitar chord progression PDFs readily showcase variations and applications of this fundamental progression in different keys and styles. Learning this progression is a cornerstone for aspiring songwriters and musicians. The Roman numeral system provides a key-independent representation. I represents the tonic (major chord in the key), IV the subdominant (major chord four notes above the tonic), V the dominant (major chord five notes above the tonic), and vi the submediant (minor chord six notes above the tonic). This structure creates a satisfying harmonic movement, underpinning the success of countless chart-topping hits.
Other Diatonic Progressions
Beyond the ubiquitous I-IV-V-vi progression, a wealth of other diatonic chord progressions offer diverse harmonic possibilities. These progressions, utilizing chords exclusively from the diatonic scale of a given key, provide a strong sense of tonal coherence. Exploring these progressions expands your harmonic palette and allows for richer, more nuanced musical expression. Many guitar chord progression PDFs and online resources detail these progressions, often categorized by their characteristic movements. Some common examples include the ii-V-I progression, known for its strong resolution, and variations incorporating the vi chord for added color. Experimenting with different chord voicings and inversions within these progressions adds further depth and texture to your playing. The use of seventh chords also greatly enhances harmonic sophistication. Understanding the relationships between chords within the diatonic scale is crucial for creating compelling and satisfying musical passages. These progressions form a solid foundation for developing your compositional skills and improvisational fluency.
Non-Diatonic or Modal Progressions
Stepping beyond the confines of diatonic harmony, non-diatonic or modal progressions introduce chords from outside the key, creating a richer, more colorful sonic landscape. These progressions often borrow chords from parallel keys or modes, resulting in unexpected harmonic twists and turns. The use of borrowed chords adds tension and release, leading to a more dynamic and engaging musical experience. Guitar chord progression PDFs and online tutorials frequently showcase these progressions, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications. Common examples include the use of secondary dominants, which function as temporary dominant chords leading to a chord other than the tonic, and the incorporation of diminished chords for dramatic harmonic shifts. Mastering non-diatonic progressions requires a deeper understanding of music theory, specifically the relationships between different keys and modes. Exploring these progressions expands your compositional vocabulary and allows you to create music that is both sophisticated and expressive. The ability to effectively utilize non-diatonic chords is a hallmark of skilled musicians.
Advanced Chord Progressions
Exploring advanced techniques significantly expands harmonic possibilities. Mastering secondary dominants and employing 7th and diminished chords adds sophistication and complexity to your playing. These techniques unlock new avenues for creativity and expression in your music.
Using Secondary Dominants
Secondary dominants are borrowed chords that add a powerful, temporary harmonic shift. They function as dominant chords (V chords) leading to chords other than the tonic. For instance, in the key of C major, a G7 (V chord) leads to C major (I chord). However, a D7 (V of G) functioning as a secondary dominant can powerfully lead to a G major chord. This creates a strong pull and adds a sense of anticipation. The effect is a more dramatic and less predictable progression. The secondary dominant resolves to its related chord, creating a pleasing resolution. The use of secondary dominants adds a layer of sophistication, making your chord progressions richer and more interesting. They are a staple in jazz, blues, and pop music, adding a dynamic element. To master secondary dominants, practice identifying the V chord of each chord in a progression. This allows you to strategically place secondary dominants to create unexpected and satisfying harmonic movement. Experiment with different voicings and inversions for added texture. The possibilities are truly endless.
Employing 7th Chords and Diminished Chords
Incorporating 7th chords and diminished chords significantly enriches the harmonic landscape of your progressions. 7th chords, adding a seventh note to a basic triad, create a more complex and sophisticated sound. Major 7th chords sound bright and jazzy, while dominant 7th chords (with a minor 7th) possess a strong, bluesy feel. Minor 7th chords offer a melancholic or pensive quality. Experiment with different types of 7th chords to color your progressions. Diminished chords, with all three notes a minor third apart, generate a sense of tension and instability, often used as passing chords or to create chromatic movement. They resolve strongly to other chords, creating a satisfying harmonic resolution. Diminished chords add a unique flavor, especially in jazz and more modern styles. The combination of 7th chords and diminished chords unlocks a wide range of expressive possibilities. They are not just for advanced players; even simple applications can significantly enhance your music’s harmonic depth and interest. Explore using them in your progressions to find new and exciting sounds.
Resources for Learning Chord Progressions
Numerous resources are available to help you master chord progressions. Explore guitar chord progression PDFs, online tutorials, and video lessons. These tools offer structured learning and practical examples to accelerate your progress; Many free and paid options cater to all skill levels.
Guitar Chord Progression PDFs and Charts
Guitar chord progression PDFs and charts offer a structured approach to learning. These resources often visually represent chord progressions, making them easy to understand and follow. Many freely available PDFs provide various progressions categorized by genre or complexity, perfect for beginners. Others offer more advanced progressions, including those incorporating seventh chords, diminished chords, or secondary dominants. These charts are excellent for practicing fingerings and transitions between chords. The visual nature of PDFs and charts aids in memorization and allows for quick reference during practice sessions. They can be printed for offline use, making them ideal for learning on the go. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced guitarist, well-designed guitar chord progression PDFs and charts can significantly improve your understanding and playing.
Online Tutorials and Videos
The internet offers a wealth of online tutorials and videos dedicated to teaching chord progressions. These resources provide a dynamic learning experience, often incorporating visual and auditory elements. Many platforms, such as YouTube, offer free lessons ranging from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced techniques. These videos frequently demonstrate chord voicings, fingerpicking patterns, and strumming techniques. Interactive tutorials allow users to practice alongside the instructor, receiving immediate feedback. Some online platforms offer structured courses with quizzes and assignments, providing a more formal learning structure. These videos often cover different musical genres, showing how chord progressions are used in various styles. Furthermore, online tutorials often include downloadable resources, such as chord charts or backing tracks, enhancing the learning process; This readily accessible format allows for flexible and self-paced learning.
